Walker-Wang Models
A generalisation of string-net models has been recently given in terms of the Walker-Wang models . These models allow non-trivial braiding of the charges giving a rich behaviour in their bulk and at their boundary.
The entanglement spectrum for topologically trivial cuts of a Walker-Wang model can be found in the same way as for string-nets given by
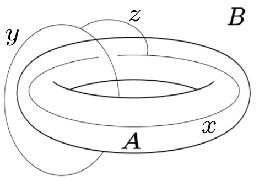
Nevertheless, partitions with non-trivial boundary topology reveal novel correlation properties. To identify their effect on the interaction distance we take the region with a boundary topologically equivalent to a torus, as shown in the figure below. Among the allowed configurations in the ground state is a braiding of loops with charges
and
supported in
and
respectively, connected by a string of charge
piercing
. Thus, the probability spectrum should now encode information about the non-trivial braiding of the charges.
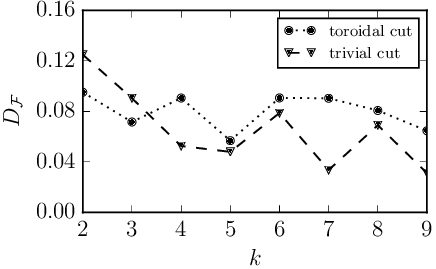
In the second figure below we show for toroidal cuts of non-Abelian SU(2)
Walker-Wang models as a function of the level
. Compared to the spherical cut we see that the interaction distance depends not only on the geometry of the cut but also on the topology of
. Its non-zero value indicates the necessity of interactions for the existence of non-Abelian topological order also in three dimensions.